In today's fast-paced business environment, the amount of information generated and shared escalates continuously. With so much data to manage, it's unsurprising that many organizations struggle to maintain document control.
In fact, according to a study conducted by Regus, 68% of Philippine businesses have lost a contract or client in the past year due to poor document management practices.
This statistic emphasizes the importance of effective document management practices in the Philippines and understanding the document life cycle to ensure that documents are accurate, relevant, and secure throughout their lifetime.
We at UNAWA have recognized this market gap and set out to address it by writing a detailed guide covering all aspects of the document life cycle.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve deeper into the different stages of the document life cycle and discuss the best practices for managing documents in each stage within an organization.
So if you're ready, let's get started!
What Is Document Life Cycle Management?
Document life cycle management or DLCM is the process of managing a document throughout its entire life cycle, from creation to archiving or disposal. Because it outlines the procedures for handling documents, business decision-makers regard it as an essential component of a company's content management strategy.
DLCM typically consists of several stages, with the five most common being creation, storage, retrieval, distribution, and archival and disposal.
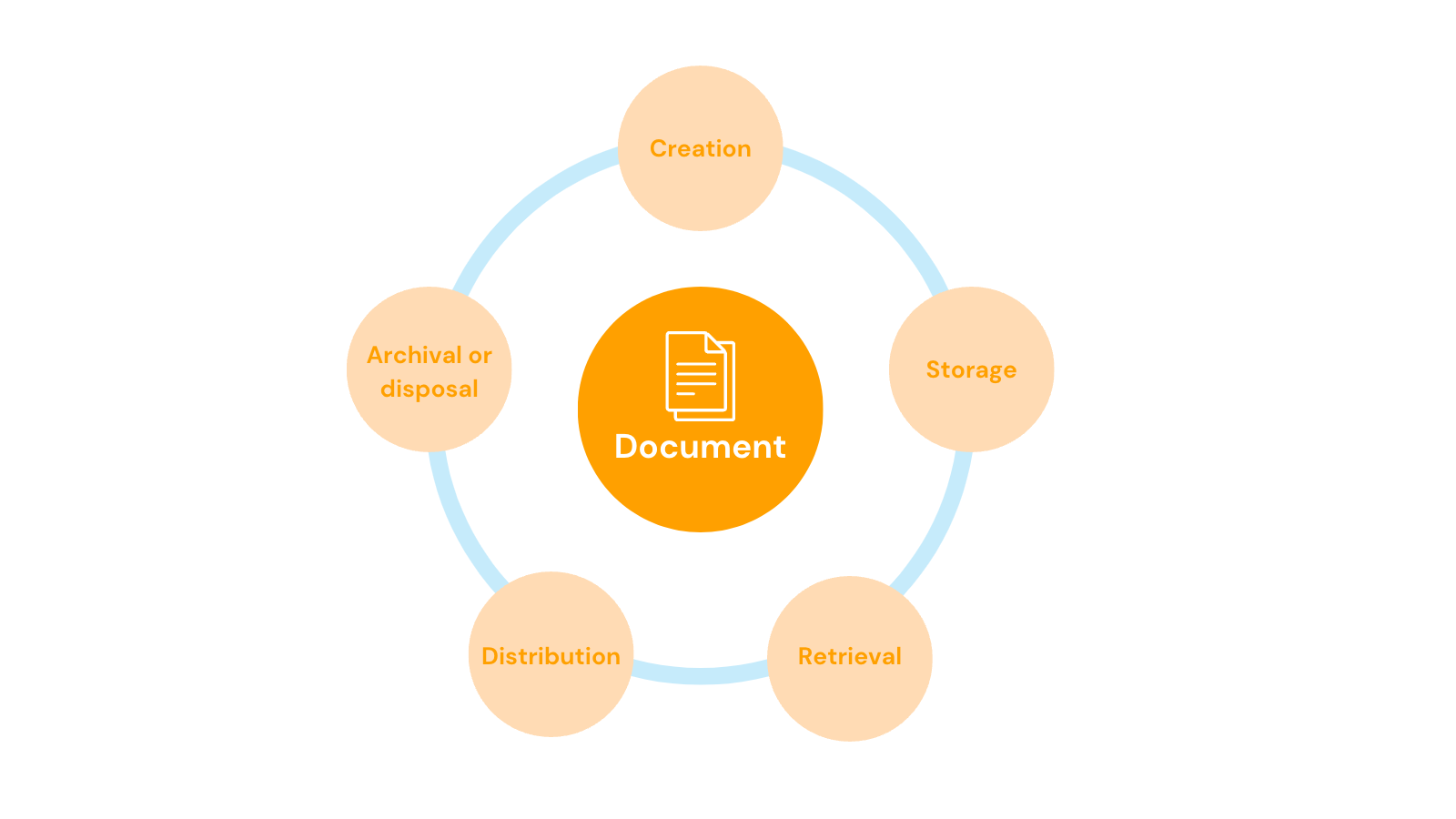
These document lifecycle stages are universal to all organizations. However, these stages can be modified based on the requirements of the business. Optionally, additional stages may be added, such as document approval and workflow-related processes.
Furthermore, each stage has distinct characteristics to ensure that documents adhere to the enterprise's established standards. In most cases, documents move back and forth between these stages.
Stages of Document Life Cycle
Having a system in place to efficiently manage documents is essential to the success of any company. Whether it's a contract, a report, a proposal, or some other type of document, knowing how it moves through its life cycle can help you keep it up-to-date, useful, and safe at all times.
With that, let's go over each step by step so you can have a better understanding of their nature and purpose.
Creation
The creation stage of the document life cycle is the first stage in which a document is created. It entails gathering and storing the necessary information in a physical or electronic system.

During this stage, capturing accurate and complete information, including metadata such as the title, author, date, and subject, is critical.
Effective document creation strategies ensure that documents are well-organized and contain all necessary information, laying the groundwork for the document management process.
Documents that are properly created can improve overall efficiency and productivity by ensuring that information is easily accessible and organized.
That's why we recommend that businesses implement a digital document creation process to ensure efficient and accurate document production. This not only reduces manual tasks like printing, scanning, and photocopying, but it also enables remote real-time collaboration.
Storage
During the storage stage of the document life cycle, documents are kept with the intention of using them in the future. At this stage, you have you have the option store them either physically or digitally.

Physical storage is typically accomplished through the use of file cabinets or storage boxes, whereas digital storage is accomplished through the use of document management software, cloud storage systems, or other digital storage platforms.
Documents must be stored in a manner that ensures their preservation and accessibility, with adequate security measures in place to safeguard them against loss or theft.
Establishing proper storage protocols to maintain document integrity and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, such as document retention policies and data protection laws, is essential.
To maximize efficiency and productivity, storing documents in a way that allows quick retrieval and use is vital—which brings us to the next stage of DLCM...
Retrieval
The document life cycle's retrieval stage involves searching for and retrieving a previously stored document. This stage requires indexing and organizing the document to be easily searched.

A well-organized document management system that allows for easy indexing, searching, and retrieval is required for efficient document retrieval.
Documents can be searched and retrieved using various search methods, including keyword, metadata, and full-text searches.
In some cases, requesting the document from a physical storage location, such as a file cabinet or archive, may be part of the retrieval process.
By ensuring that documents are quickly and easily accessible to those who require them, efficient document retrieval improves overall efficiency and productivity.
Distribution
During the distribution stage of the document life cycle, the document is shared with the intended audience. This could include sending physical copies or distributing the document electronically via email, file sharing, or other electronic platforms.

Ensuring the document is securely and efficiently distributed to the intended audience is critical.
Proper distribution can improve organizational collaboration and communication by ensuring all stakeholders can access the necessary information.
Establishing clear protocols for sharing documents, using secure sharing platforms, and providing clear instructions for accessing and using the document are all examples of effective distribution strategies.
Archival or Disposal
During the archiving or disposal stage of the document life cycle, documents are kept for long-term storage or thrown away when they are no longer needed.

For archiving, documents are moved to a safe place where they are kept for future use. For disposal, documents no longer required are disposed of safely, such as by shredding or deleting them.
Documents are usually archived or disposed of based on legal and regulatory requirements or the document's value to the organization.
As a result, proper archiving and disposal procedures are required to ensure that legal and regulatory requirements are met, sensitive information is safeguarded, and storage costs are managed.
Effective archiving and disposal strategies increase overall efficiency and productivity by ensuring that documents are managed and stored correctly throughout their lifecycle.
The Importance of Effective Document Life Cycle Management
Document lifecycle management is critical for keeping documents organized, accessible, and secure. A well-defined document life cycle is crucial for increasing overall efficiency and productivity, reducing risk, and meeting legal and regulatory requirements.
Efficiency and Productivity
Businesses in the Philippines can significantly benefit from adopting a DLCM strategy by implementing well-defined procedures.
By doing so, organizations can ensure that documents are managed to maximize productivity while minimizing waste and redundancy.
One key best practice is using consistent templates for document creation. This allows businesses to save time and ensure that documents are standardized, making them easier to read and understand.
In addition, auto-filling information in templates can reduce human error in encoding, further increasing efficiency and accuracy.
If documents are appropriately managed throughout their life cycles, they will be well-organized and easy to find—increasing productivity. In turn, this can help workers collaborate and make quicker, better-informed decisions. As an added bonus, document life cycle management frees up resources by reducing the likelihood of mistakes, duplication, and inefficiency.
By digitizing and automating document management procedures, productivity and efficiency can be increased even further. As a result, workers may be freed up to concentrate on more strategic, profit-generating endeavors.
Information Security and Privacy
With the rise of cyber threats and data breaches, information security and privacy have become pressing issues in the Philippines.

The Data Privacy Act of 2012 establishes stringent requirements for collecting, using, storing, and disposing of personal information by organizations operating in the Philippines.
If you ignore these regulations, you may face serious repercussions, including jail time and heavy fines.
To meet these standards, efficient document life cycle management is crucial, as it guarantees that private information is handled under privacy laws and regulations. Effective information security and privacy strategies can also aid businesses in gaining the trust of their customers, employees, and other stakeholders, which can boost their reputation and lessen the potential for irreparable harm to that reputation from data breaches or non-compliance with privacy regulations.
Ultimately, businesses in the Philippines can only stay honest and competitive if they take data protection and privacy seriously.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
While information security and privacy are unquestionably crucial to meeting regulatory requirements, efficient DLCM can also help with that front by making it easier to meet documentation and record-keeping obligations.
Not only does it reduce the likelihood of violations due to missing or insufficient records, but it also ensures that all required documentation is produced, maintained, and archived correctly.
Moreover, effective DLCM can help businesses comply with document retention and destruction regulations.
This is particularly important for companies operating in highly regulated industries, where document retention and destruction regulations are particularly stringent, such as:
- Finance
- Healthcare
- Tourism
- Legal Services
Overall, effective document life cycle management can help businesses avoid costly penalties, lawsuits, and other legal and financial risks by improving legal compliance. Additionally, maintaining proper documentation can help companies to establish a strong defense during legal disputes, reducing the risk of reputational damage and other negative consequences.
Document Life Cycle Management Best Practices
The preceding section provided an in-depth analysis of DLCM's value to businesses, particularly in the Philippines. Now, let's dive into some practical advice for applying best practices throughout the document life cycle.
1. Creation Stage
- Clearly define the purpose and audience of the document before creating it.
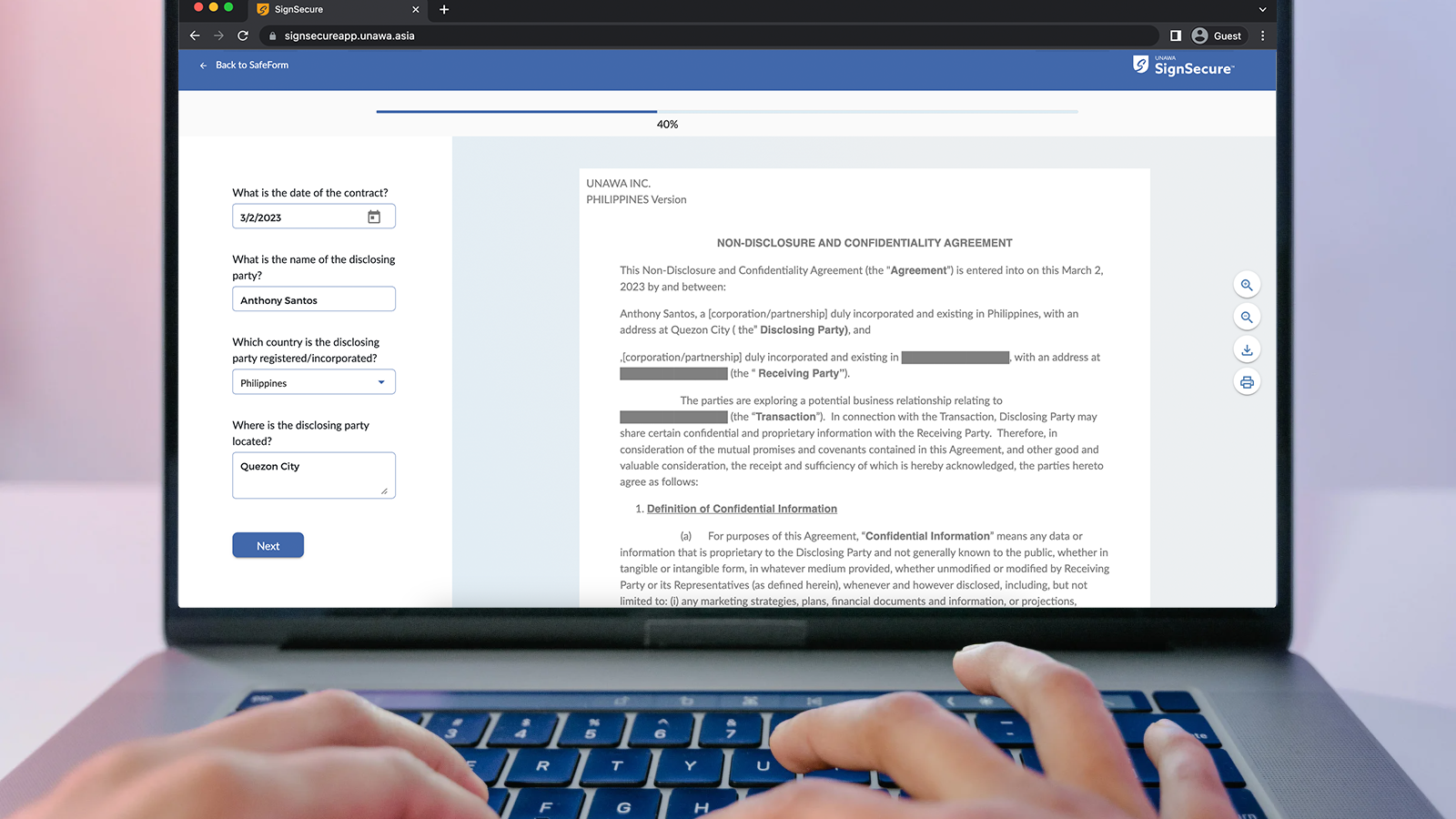
- Establish templates and style guides, like what our UNAWA SafeForm™ offers, to ensure consistency in formatting and structure.
- Use version control to track changes and revisions.
- Implement a review and approval process to ensure accuracy and completeness.
2. Distribution Stage
- Establish appropriate access controls to ensure only authorized individuals can access the document.
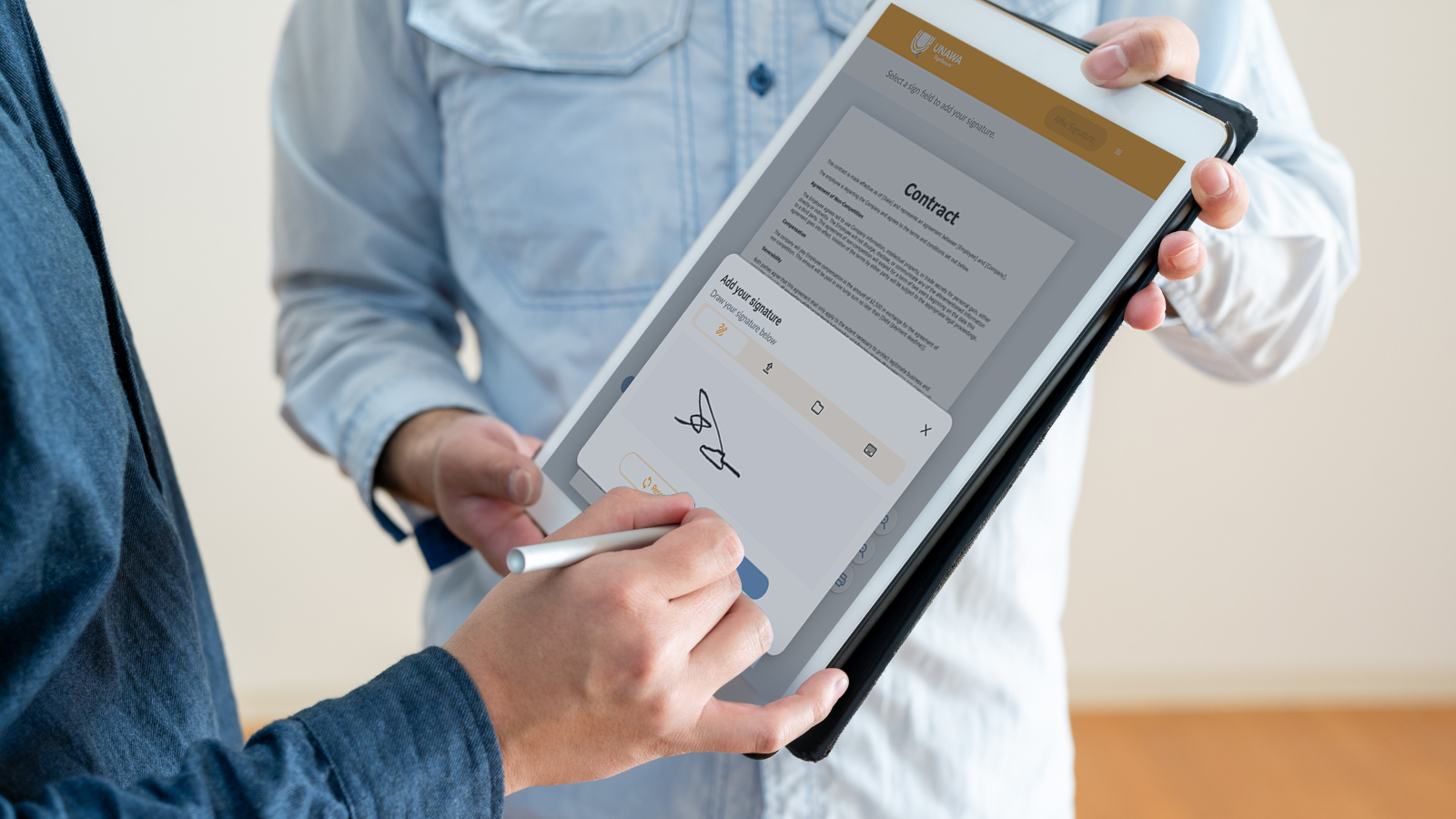
- Use digital signature software such as UNAWA SignSecure™ and other encryption techniques to increase the security of documents and decrease the risk of fraud.
- Monitor document access and use it to detect any unauthorized activity.
3. Storage Stage
- Use a centralized document management system, such as our upcoming solution UNAWA ForMA™, to ensure consistency in file organization and naming conventions.
- Regularly back up document repositories to prevent data loss.
- Establish retention schedules to ensure that documents are kept only as long as necessary.
- Implement appropriate security controls to protect documents from unauthorized access or theft.
4. Retrieval Stage
- Use metadata to tag and categorize documents for easy searching and retrieval.
- Implement an indexing system to facilitate quick and efficient document retrieval.
5. Archival or Disposal Stage
- Establish appropriate retention policies to ensure that documents are kept only as long as necessary.
- Use secure methods for document destruction, such as shredding or secure digital deletion.
- Keep a record of all disposed of documents for auditing purposes.
To find out more about best practices for each phase of the document life cycle, tune in to this episode of The Moonlock Podcast with Atty. Gino Jacinto, COO and VP of Operations and Business Development of UNAWA.
Conclusion
Document life cycle management is a critical process that ensures an organization's efficient and effective document management. Each stage of the DLCM should be well-defined, implemented consistently, and structured. This approach assists organizations in meeting legal and regulatory requirements, increasing productivity and efficiency, and protecting data security and privacy.
As such, we encourage all businesses to take advantage of the benefits of proper document life cycle management. By partnering with UNAWA and implementing the best practices discussed in this guide, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, productivity, and security in their document management practices.
Contact us today to learn more about how your business better manages your documents throughout their entire life cycle.

